Variable & Data Type
1. Saving Values
Intructions :
Save the result of (42 - 11) * 22 to result.
Print result.
2. Variable
Instructions :
Store the value 15 in a variable named a_value.
Store the result of (25 - 7) * 17 to a variable named a_result.
Using the print() command, display the following:
The value stored in the a_value variable.
The result of adding 12 to the variable a_result.
The result of adding a_value to a_result.
3. Variable Names
Instructions :
In the code editor on the right, we attempted to store 34000 in a variable named old-income, and 40000 in a variable named new income. But both of these variable names cause syntax errors, so we commented-out the code.
Change the variable name old-income to old_income to prevent a syntax error.
Change the variable name new income to new_income to prevent a syntax error.
Remove the # from each line so that the code will run, then run the code.
4. Updating Variable
Instructions :
Update the variable income by adding 6000 to its current value.
The variable income is already shown in the code editor on the right.
Print income.
Assign a value of 20 to a variable named variable_2.
Update the value of variable_2 by adding 10 to its current value. You can take advantage of the += operator.
Update the value of variable_1 by multiplying its current value by 4. You can take advantage of the *= operator.
Display variable_1 and variable_2 using print().
6. Integers & Floats
Instructions :
Assign the integer 10 to a variable named variable_1.
Assign the float 2.5 to a variable named variable_2.
Update the value of variable_1 by adding the float 6.5 to its current value. You can use the += operator.
Update the value of variable_2 by multiplying its current value by the integer 2. You can use the *= operator.
Display variable_1 and variable_2 using print().
Assign the value 2.8 to a variable named variable_b.
Round variable_a using the round() command, and assign back the rounded value to variable_a.
Convert variable_b from a float to an integer using the int() command, and assign back the converted value to variable_b.
Display variable_a and variable_b using the print() command.
Assign the string 4.0 to a variable named average_rating. Make sure you don't mistake a string for a float.
Assign the string 1724546 to a variable named total_ratings. Make sure you don't mistake a string for an integer.
Assign the string free to a variable named price.
Display the app_name variable using print().
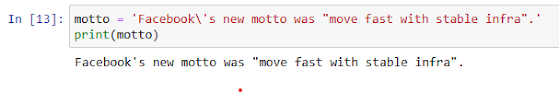
Notice there's a . character at the end of Facebook's new motto is "move fast with stable infra." — you'll need to include the . character in your answer.
Display the variable motto using print() — displaying motto is required for answer checking.
10. String Operations
Assign the float 3.5 to a variable named fb_rating.
Convert fb_rating from a float to a string using the str() command, and assign the converted value to a new variable named fb_rating_str.
Concatenate the strings stored in facebook and fb_rating_str to form the string Facebook's rating is 3.5.
Assign the concatenated string to a variable named fb.
You'll need to add a space character between Facebook's rating is and 3.5 to avoid ending up with the string Facebook's rating is3.5.
Display the fb variable using print() — this is required for answer checking.









Komentar
Posting Komentar